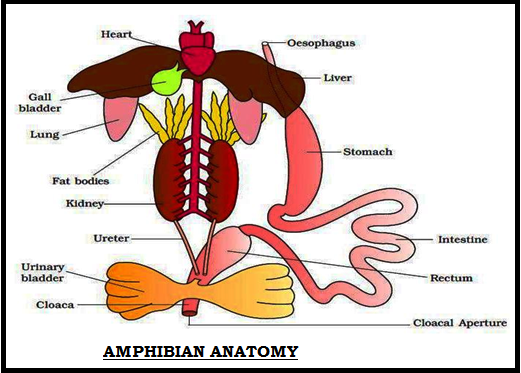
CLASS AMPHIBIA: A) INTRODUCTION

● `color{maroon}"Habitat"`: As the name indicates (`color{Violet}"Gr., Amphi : dual, bios, life"`), amphibians can live in aquatic as well as terrestrial habitats.
● `color{maroon}"Morphology"`:
● `color{maroon}"Body Structure"`:
`star` Most of them have `color{Violet}"two pairs"` of limbs.
`star` Body is divisible into `color{Violet}"head and trunk"`.
`star` Tail maybe present in some.
`color{maroon}"Sense Organs"`:
`star` The amphibian skin is `color{Violet}"moist"` (without scales).

`star` The eyes have `color{Violet}"eyelids"`.
`star` A `color{Violet}"tympanum"` represents the ear.

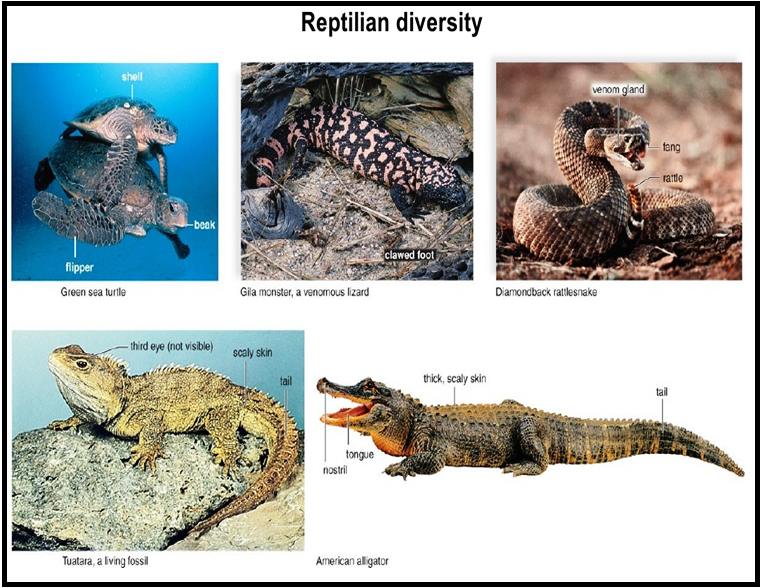
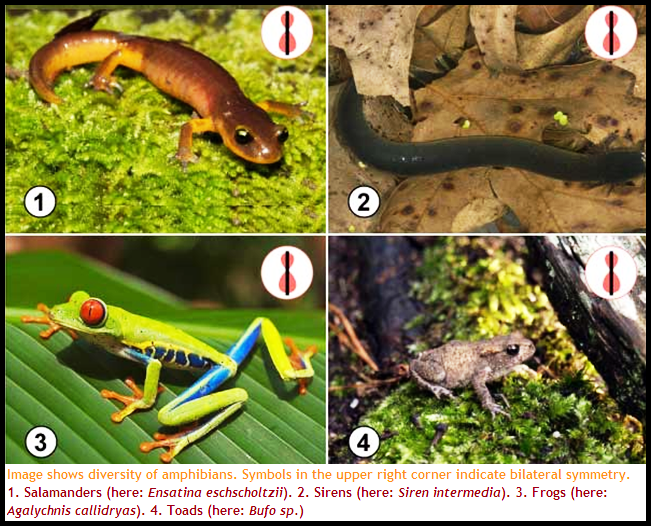
● `color{Brown}"Examples"`: Bufo (Toad), Rana (Frog), Hyla (Tree frog), Salamandra (Salamander), Ichthyophis (Limbless amphibia).
● `color{maroon}"Morphology"`:
● `color{maroon}"Body Structure"`:
`star` Most of them have `color{Violet}"two pairs"` of limbs.
`star` Body is divisible into `color{Violet}"head and trunk"`.
`star` Tail maybe present in some.
`color{maroon}"Sense Organs"`:
`star` The amphibian skin is `color{Violet}"moist"` (without scales).

`star` The eyes have `color{Violet}"eyelids"`.
`star` A `color{Violet}"tympanum"` represents the ear.

● `color{Brown}"Examples"`: Bufo (Toad), Rana (Frog), Hyla (Tree frog), Salamandra (Salamander), Ichthyophis (Limbless amphibia).